GENERAL UROLOGY CONDITIONS AND TREATMENTS
Dr Matthew Winter treats a wide range of general urological conditions with a comprehensive range of the latest treatments
Below is a brief overview of the most common general urological conditions that Dr Matthew Winter treats.
GENERAL UROLOGY CONDITIONS AND TREATMENTS
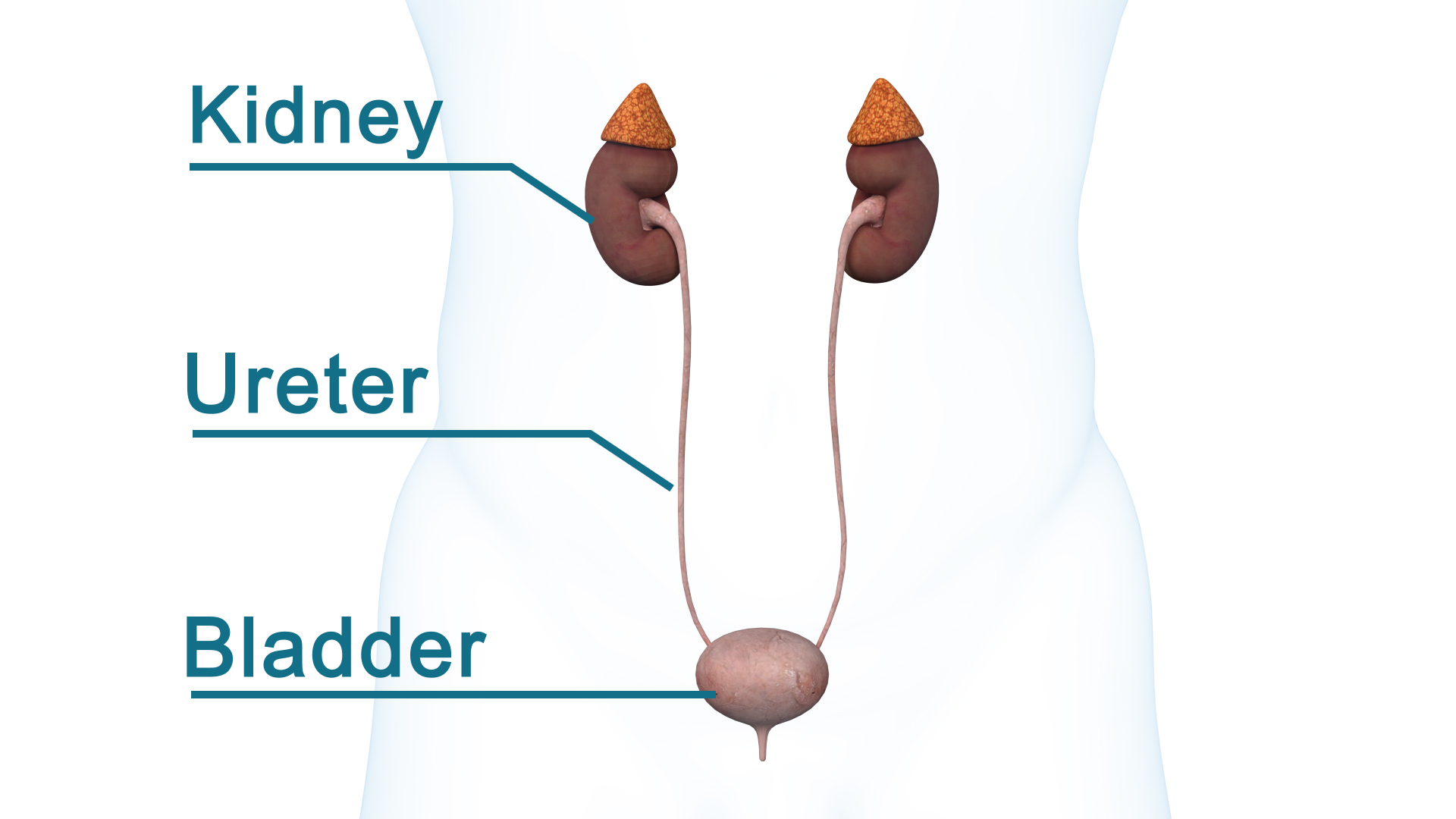
KIDNEY STONES
Kidney Stones are formed in the kidneys and are usually made of solid minerals and salt deposits. Calcium oxalate stones are the most commonly formed stones. Kidney Stones can affect any part of your urinary tract - kidneys, ureter or bladder. Kidney Stones are a common problem and approximately 5-10% of Australians suffer from them at some stage in their lives. The risk of developing kidney stones increases as you get older and if you have a family history of kidney stones. If you have had kidney stones in the past, you also have a 50% chance of experiencing another episode.
Symptoms you may notice include extreme pain in the back which can radiate to the groin “loin to groin pain”, pain on urination, pink, red or brown urine, cloudy urine or nausea and vomiting.
* If you experience fever or chills then this is an emergency situation suggesting that an infection is present. You should immediately present to your nearest emergency department.
Kidney Stones can be extremely painful and the intensity may increase as the stone moves down the urinary tract.
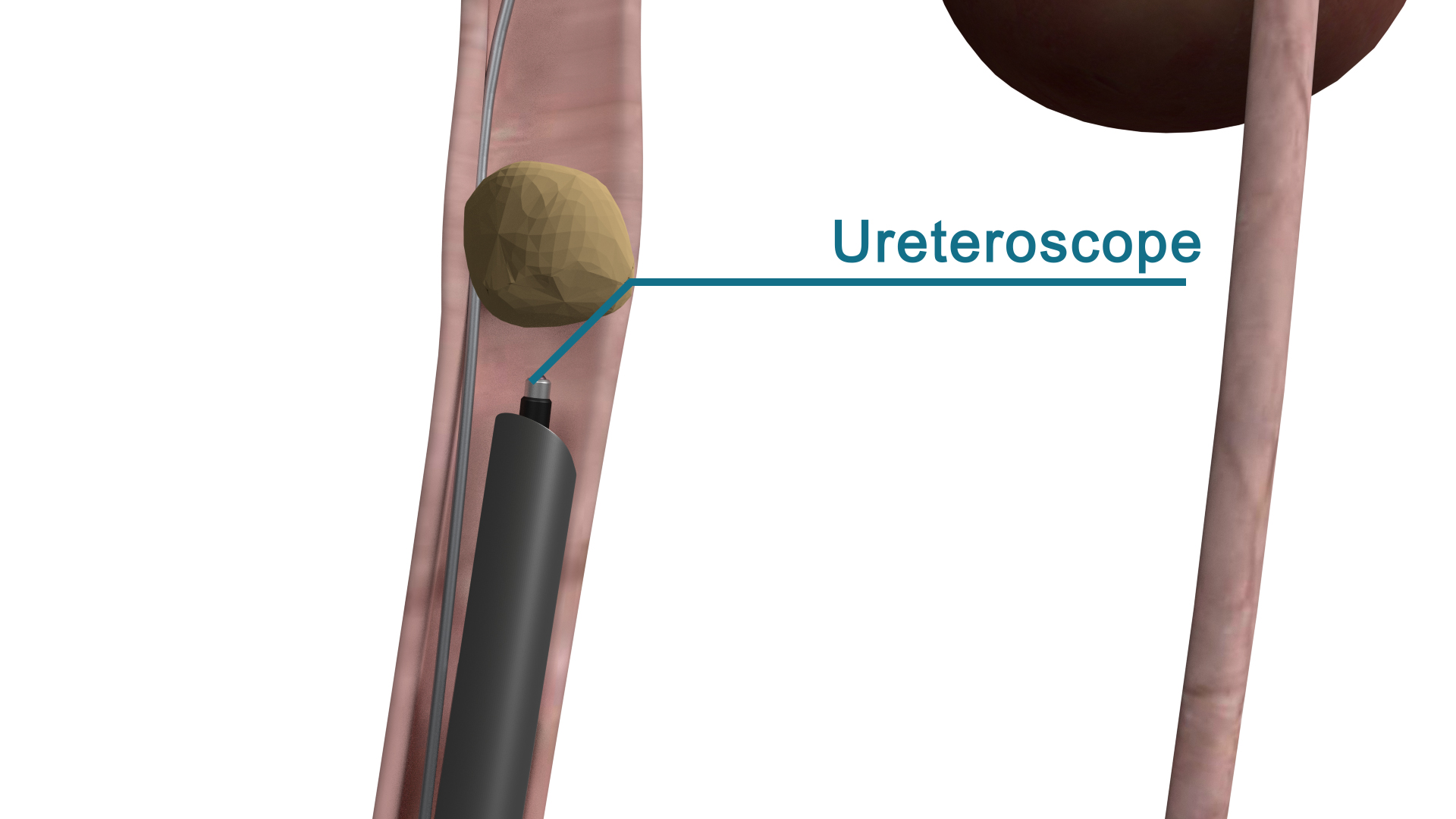
Kidney stones that fall into the ureter can cause severe pain from the break radiating to the groin
Treatment options depend upon the type of Kidney Stone, the size and location of the stone (ie kidney, ureter or bladder). If you have experienced kidney stones in the past, we may perform some urine and blood tests to assess if we can identify the cause of the stone formation and to help prevent forming stones in the future.
Smaller Stones (smaller than 5mm)
Attempt spontaneous passage of stone
Pain medications
Fluid intake
Possible stone dissolution
Follow-up imaging
Larger Stones (larger than 5mm)
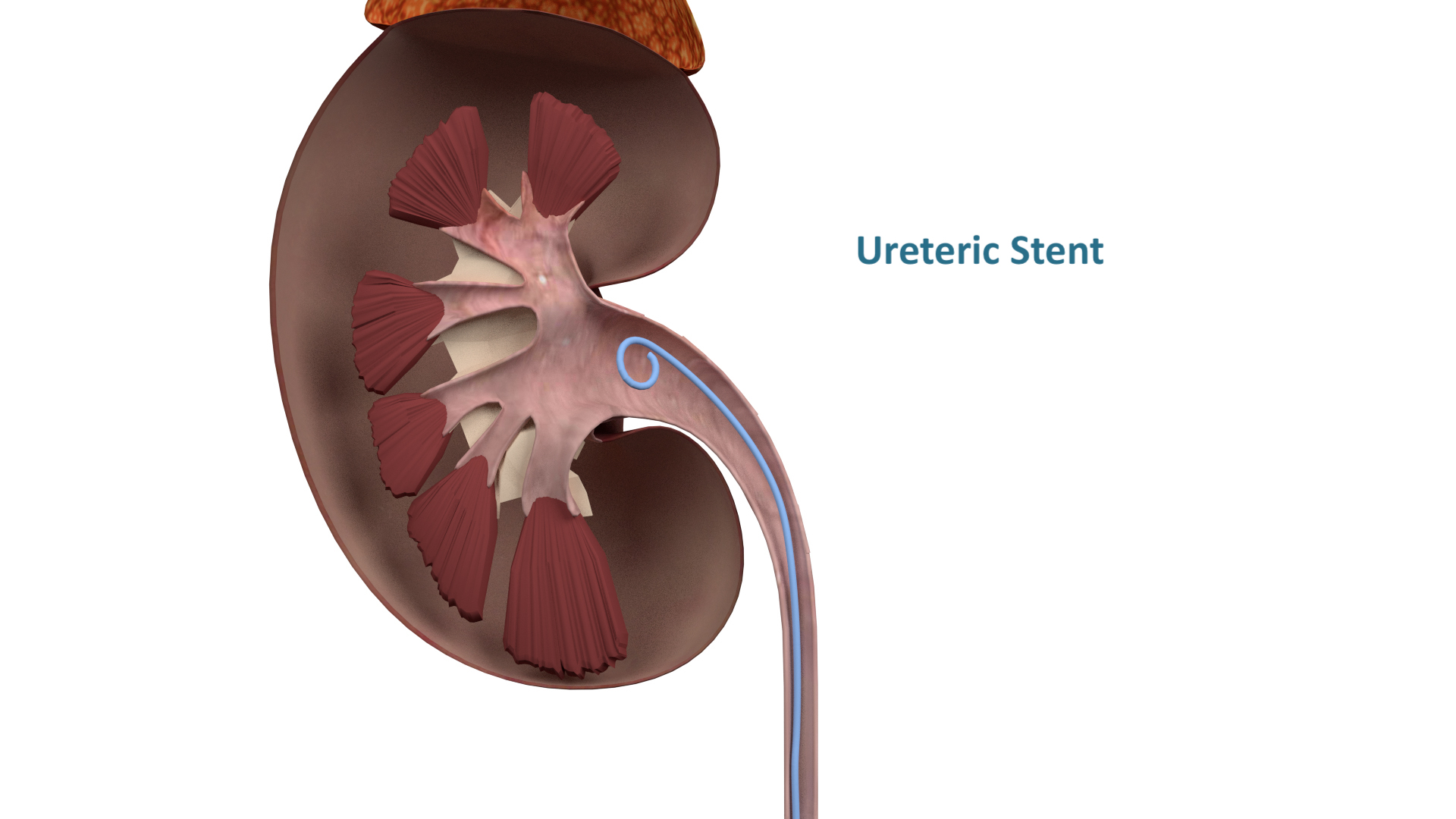
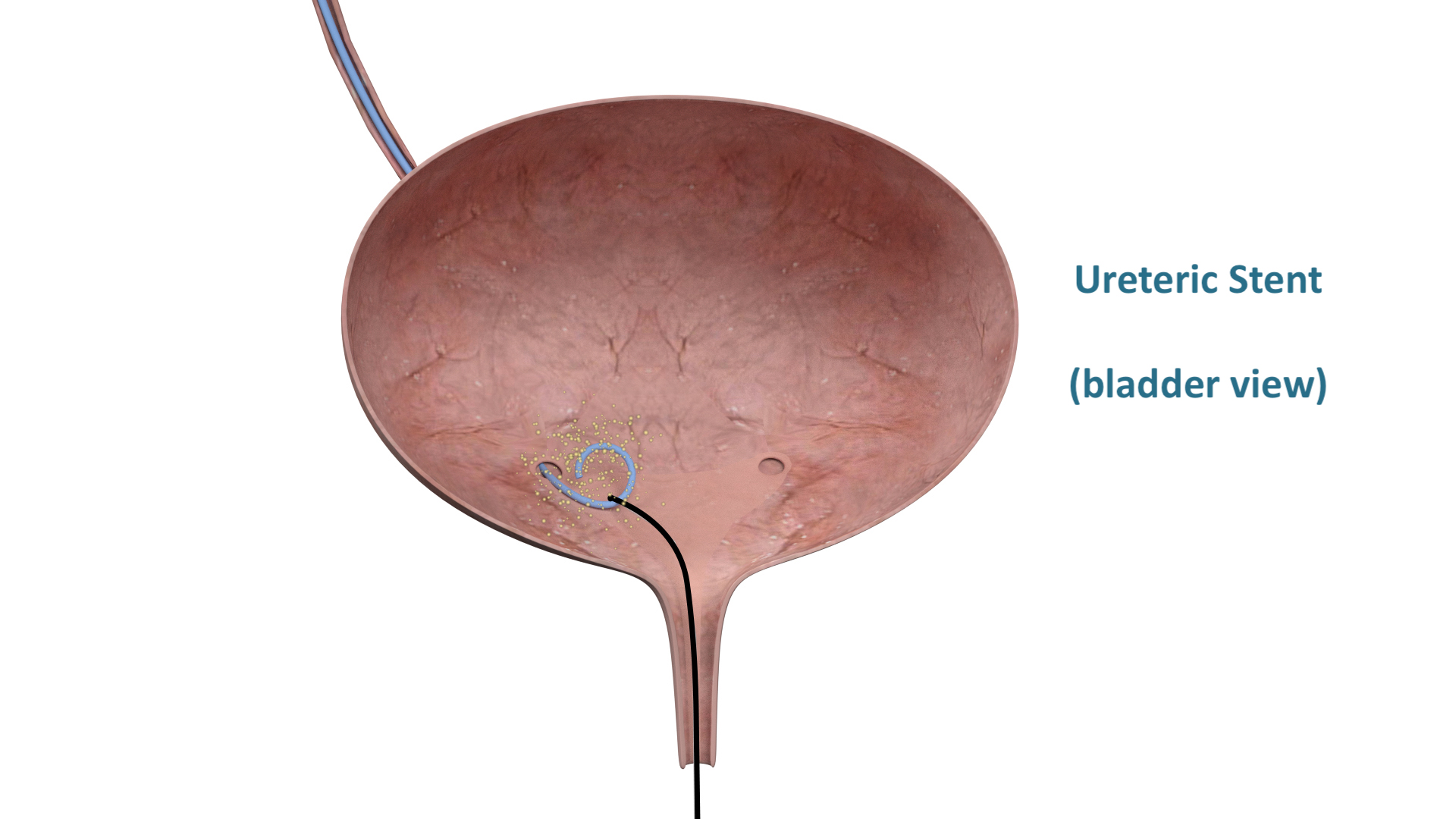
Ureteric stent (a stent is a temporary solution to unblock the kidney when a stone is stuck in the ureter. A definite procedure, listed below, is required at a later date)
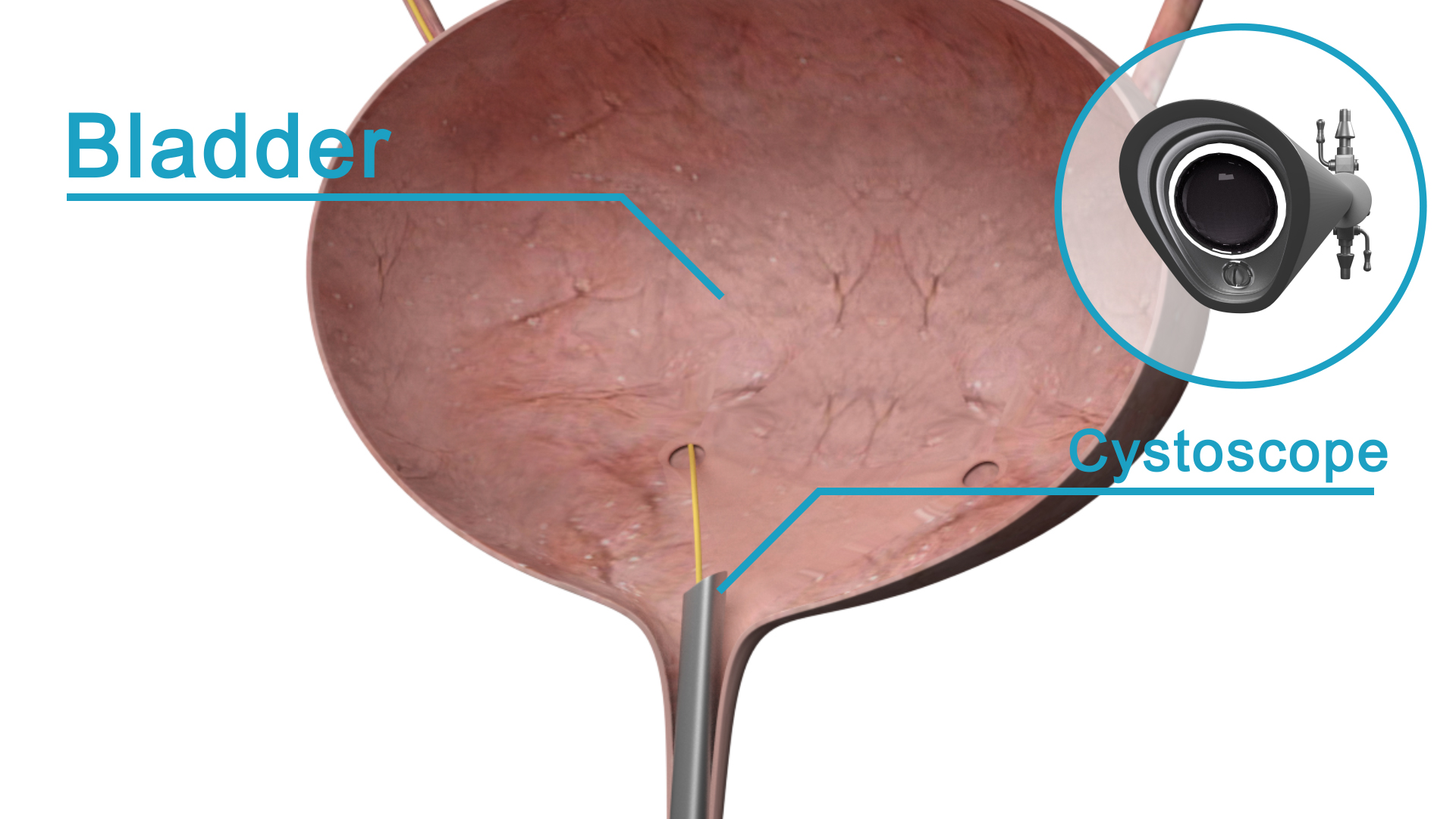
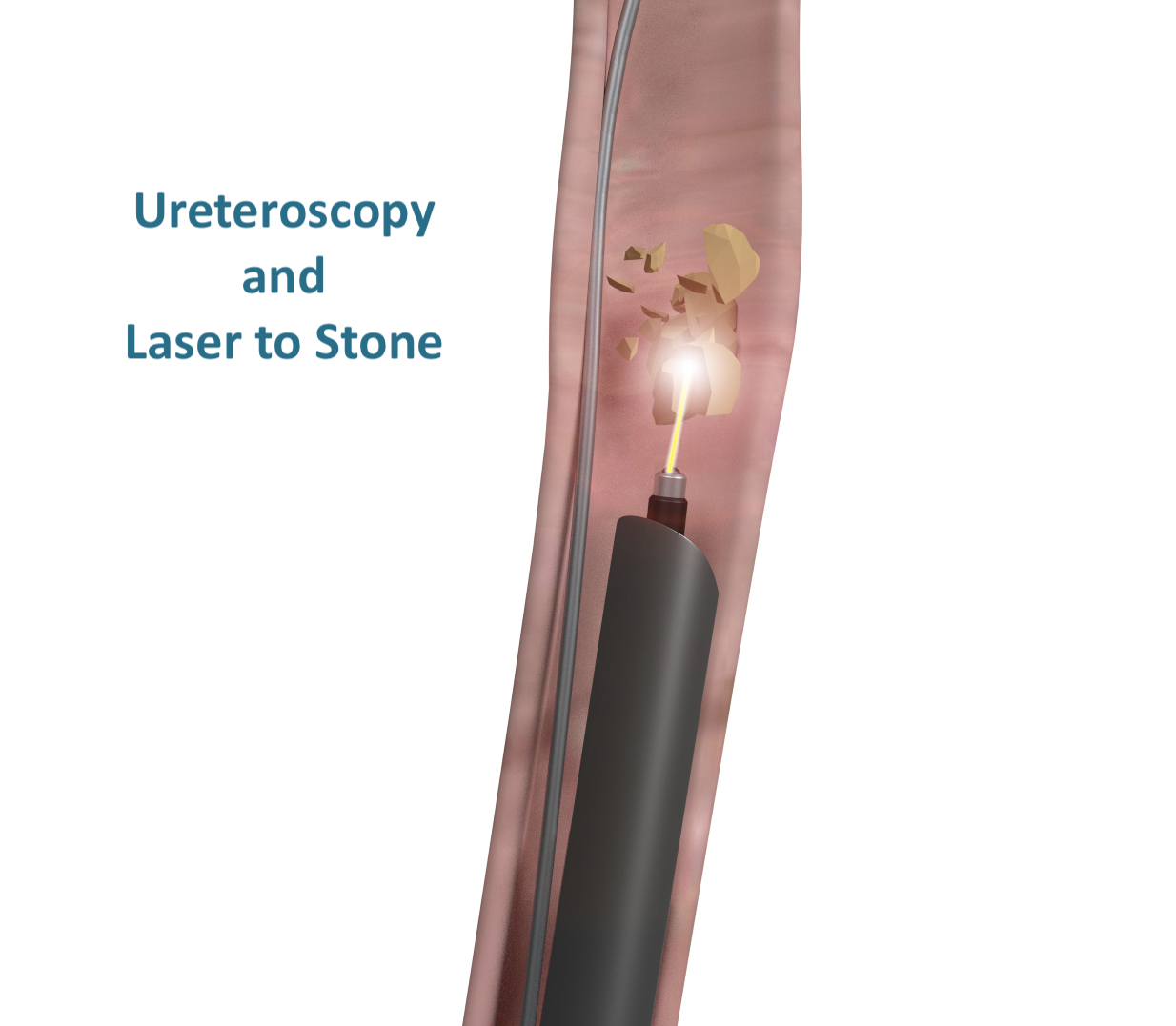
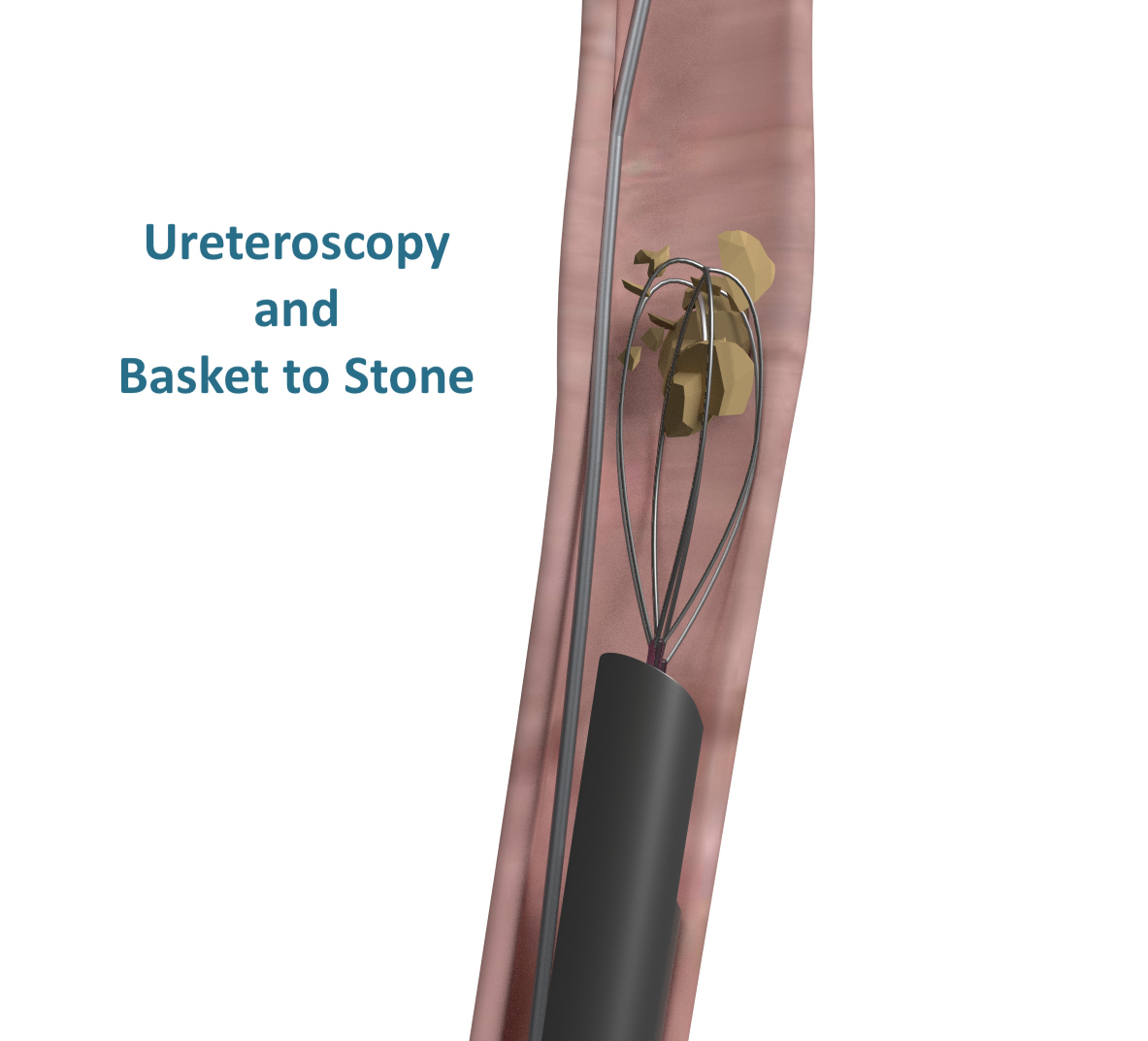
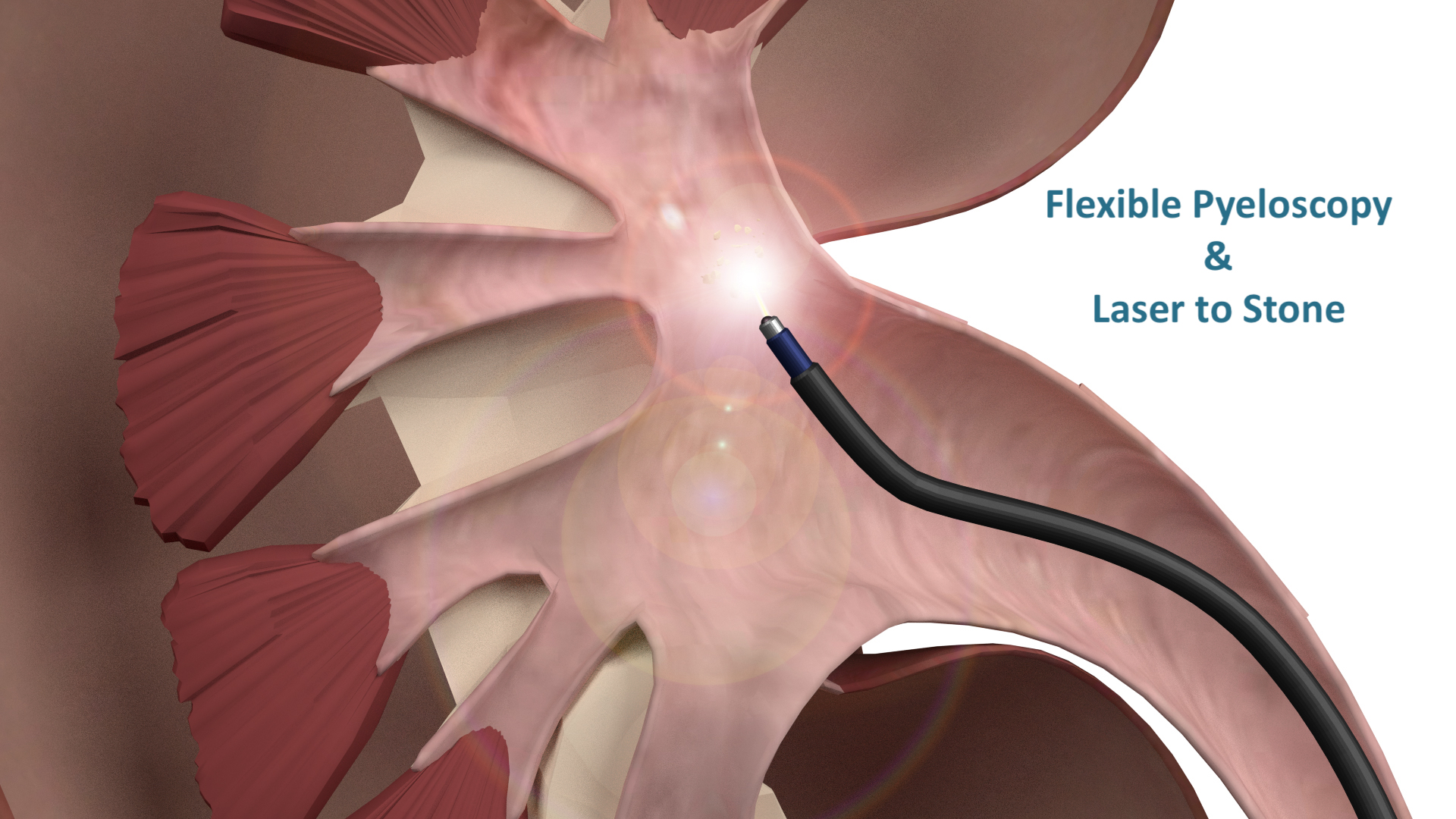
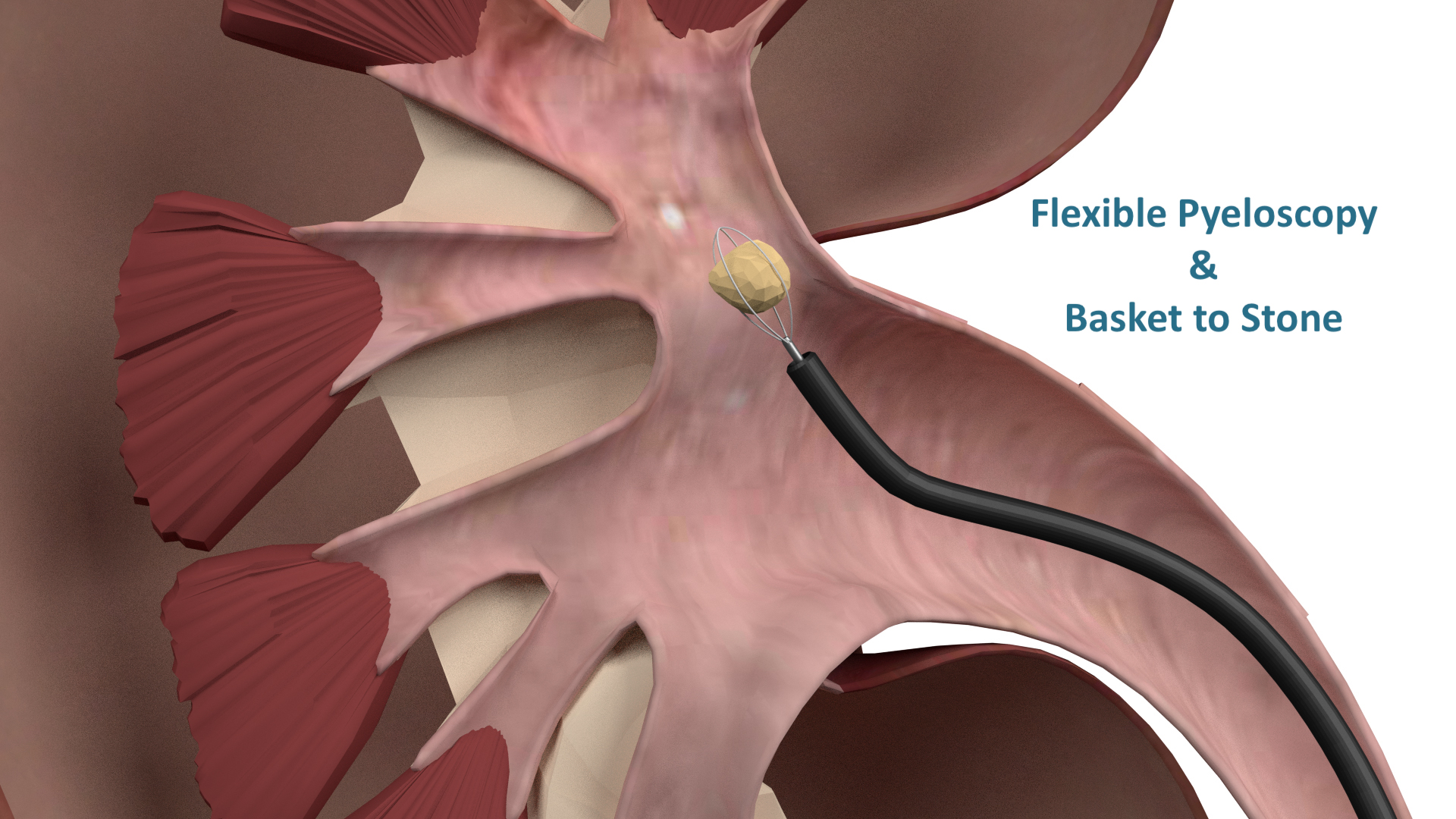
Ureteroscopy/pyeloscopy and laser
Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy (ESWL)
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) - for large stones greater than 2cm in the kidney
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact our clinic for our patient information sheet.
MENS HEALTH UROLOGY CONDITIONS & TREATMENTS
ENLARGED PROSTATE
The prostate gland is situated underneath the bladder in men. The urethra is a tube that moves urine out from the bladder to the tip of the penis. The urethra passes through the centre of the prostate gland. Prostate gland enlargement or Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) as it is also known, is a common condition that occurs amongst older males. The prostate gland continues to grow as men age which can lead to urinary problems and blockage of urine flow. The reason why the prostate gland enlarges still remains entirely unclear, however, there is some evidence to suggest it may be due to the changes in the balance in sex hormones as men age.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Symptoms that you may experience include a frequent need to urinate particularly at night time, difficulty starting to urinate, poor flow of urine with starting and stopping, dribbling at the end of urine flow, and inability to empty the bladder properly. If extreme cases, if BPH is left untreated, it can result in kidney and/or bladder failure.
Treatment options depend upon the size of the prostate, your age, your overall health and the level of discomfort you are experiencing. Treatment options include:
Medication
First line of management
Minimally invasive surgeries
Urolift
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
Greenlight laser prostatectomy
Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP)
Aquablation
Robotic surgery
Robotic simple prostatectomy (advised for larger prostate glands)
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact our clinic for our patient information sheet.
RAISED PSA
PSA is an enzyme secreted by the prostate. PSA is prostate specific but not cancer specific. The function of PSA is to liquefy semen.
The higher the value of PSA the more likely the existence of prostate cancer. The sensitivity and specificity of PSA depends on the level of PSA and the particular age of the patient. The ability of PSA to detect cancer is roughly 30%.
PSA does not differentiate between slow growing and aggressive disease but it can help to identify disease at an early stage.
Symptoms - most patients have no symptoms for their raised PSA. The symptoms patients have will depend upon the causes of the raised PSA listed below.
Cause of Raised PSA
Prostate Cancer
Enlarged prostate gland (BPH)
Infection in the prostate (Prostatitis)
Cystoscopy or Indwelling Catheter
Prostate massage (not DRE)
Acute Urinary Retention
Ejaculation
Age
Treatment
The treatment of raised PSA will be solely determined by the reason your PSA is elevated. Dr Winter will perform a comprehensive evaluation and work-up to determine the cause of your elevated PSA. He will then offer appropriate treatment options if required.
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact our clinic for our patient information sheet.
VASECTOMY
Vasectomy is a safe and effective method of birth control. This operation is only carried out when you are certain that you have fathered all the children you wish to have.
Vasectomy should be viewed as a permanent form of contraception with only a small possibility of reversibility. It is important to take time for reflection before electing to undergo vasectomy.
Vasectomy is a procedure in which the ‘Ductus deferens’ (also called the vas) are cut and blocked. The Ductus deferens are the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles to the urethra/penis to allow sperm to pass out during ejaculation.
Treatment
Vasectomy is a day procedure that can be carried out under local or general anaesthesia. It involves two tiny skin incisions in the scrotum through which the entire procedure is completed.
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact our clinic for our patient information sheet.
ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is the persistent inability to attain and/or maintain penile erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. Approximately 40-50% of men over the age of 40 years old have some degree of ED.
The causes of ED include diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, smoking, obesity, psychogenic, trauma, side effect of some medications and endocrine disorders. A common cause of ED in urology is secondary to radical prostatectomy or other pelvic surgery.
Symptoms that patients notice include inability to attain or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse.
Treatment options usually include a range of the following, including:
Treating reversible factors
Lifestyle changes - exercise, weight loss, stop smoking
Appropriate management of medical conditions
Medical therapy
Vacuum device
Intracavernosal injections (injections directly into the penis)
Penile prosthesis
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact our clinic for our patient information sheet.
LOW TESTOSTERONE
Low Testosterone can be due to testicular failure or secondary to hormonal imbalances caused by failure of the brain to make certain hormones or due to excess hormonal production (eg. prolactin). Risk factors include age, diabetes, chronic diseases, obesity, liver disease and androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) for prostate cancer.
Symptoms patients may notice include low energy levels, low mood, low libido, infertility and erectile dysfunction. Osteoporosis, obesity, breast enlargement and decreased muscle mass can also occur.
Treatment is to give testosterone replacement therapy, which may include one of the following:
Topical gel (preferred)
Patch placed on skin
Implants
Injectable
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact our clinic for our patient information sheet.
PEYRONIE’S DISEASE
(Penile Curvature)
Peyronie’s Disease is the benign curvature of the penis which is thought to occur due to repetitive micro-trauma to the penis and the build up of fibrous scar tissue formation in the tunica albuginea (TA). The TA surrounds the erectile mechanism of the penis. The plaque restricts the penis from being straight during an erection and the penis bends towards the side of the plaque. Peyronie’s disease is present in approximately 0.5-10% of the male population and tends to present around 50-55 years of age. It can cause significant pain in some men and may limit your ability to have sexual intercourse.
*Notice the plaque formation causing penile deviation
Symptoms include penile curvature during erection, a firm lump on the penis, penile pain and erectile dysfunction.
The acute phase of Peyronie’s is associated with pain and tends to last for the first 3-6months post diagnosis
The stable phase of Peyronie’s occurs when the patient no longer has pain and has stable curvature for 3 months
Treatment
Conservative - pain relief, topical therapy (creams and gels) and injections
Surgical
The aim of the operation is to reduce curvature to allow satisfactory
intercourse and minimise loss of penile length
Dr Winter will discuss the operation in detail during your consultation
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact our clinic for our patient information sheet.
PHIMOSIS
Phimosis is narrowing of the foreskin, which leads to difficulty or complete inability to retract the foreskin.
Symptoms you may notice include pain, infections or foul odour (tip of penis or urine) or difficulty with erections or sexual intercourse.
Treatment options include:
Steroid cream applied directly to the penis/foreskin - small chance of success
Circumcision - definitive treatment
For more information please don’t hesitate to contact our clinic for our patient information sheet.
SCROTAL SWELLING
Scrotal Swelling or an enlarged scrotum can be due to a range of conditions. This includes - hydrocele (fluid surrounding the testis), epididymal cyst (cyst of the epididymis), infection (epididymitis/orchitis/epididymoorchitis), testicular torsion (twisted testis), varicocele (dilation of normal testicular veins) trauma or testicular cancer.
Symptoms you may notice include swelling, pain, a hard lump or a tense/heavy feeling. If you have an infection, a warm, red scrotum may be present.
If you develop acute onset severe testicular pain, we advise that you present immediately to your nearest emergency department
Any hard lump should be investigated with an ultrasound to rule out testicular cancer
Treatment
The treatment for scrotal swelling is dependent upon the underlying cause
Dr Winter will advise the best treatment based on his diagnosis for your scrotal swelling